6th scienceECOSYSTEM FOOD CHAIN SYSTEM Biology Diagrams
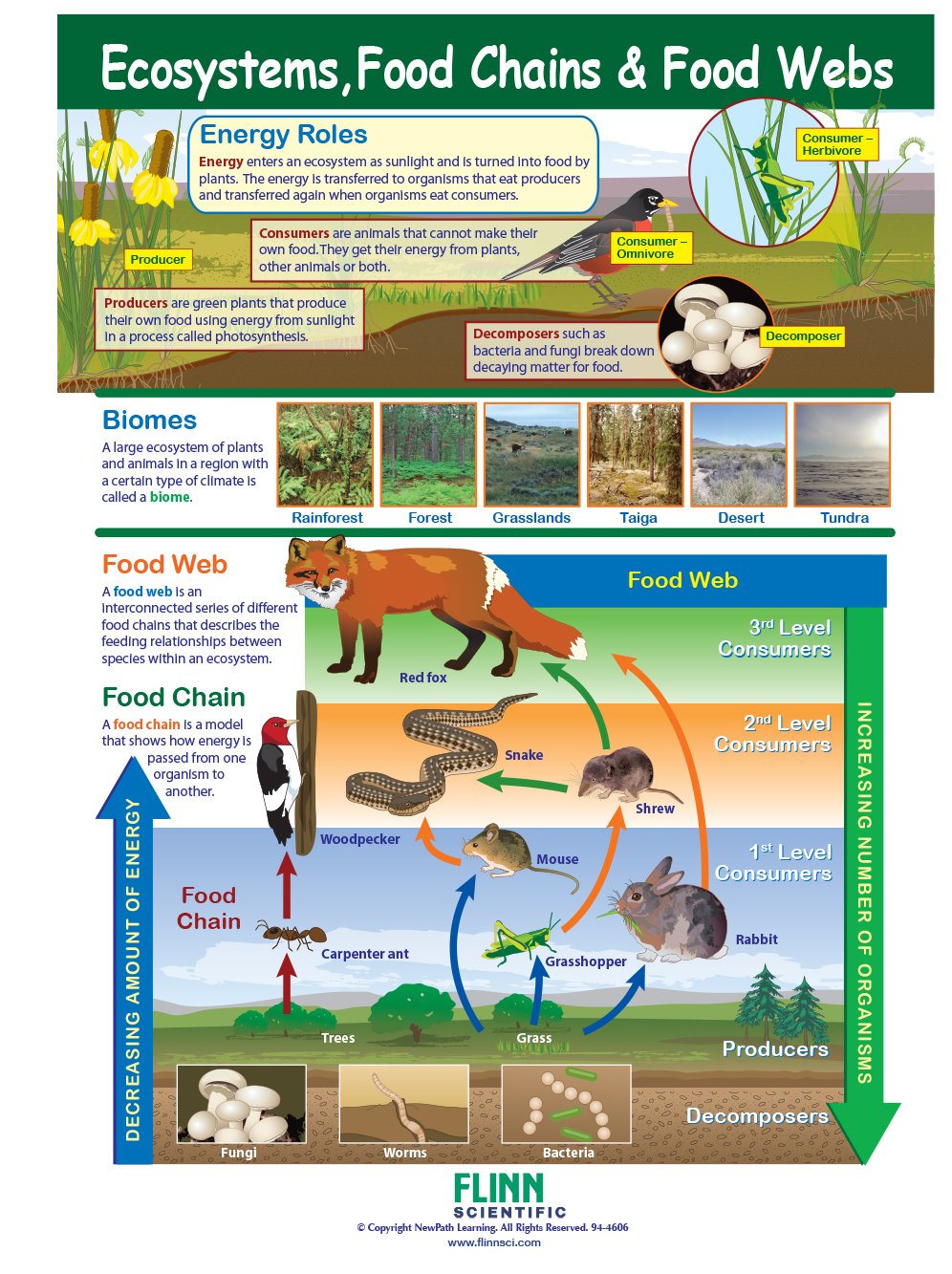
6th scienceECOSYSTEM FOOD CHAIN SYSTEM Biology Diagrams Food chains reveal the relationships between organisms, showing how each organism plays a role in maintaining ecological balance. By studying food chains, ecologists better understand ecosystem dynamics, including the flow of energy, population control, and the impact of human activities on natural habitats. The complex nature of food chains and food webs shows how important they are for promoting biodiversity and keeping ecological balance, which are key factors for environmental conservation. Food webs have many links between different species, showing how complicated ecological interactions can be and how each species is needed for ecosystem health.

Controls host populations and plays a role in ecosystem balance. Detritus Food Chain. The detritus food chain focuses on the decomposition of organic matter, as it involves organisms that break down and feed on decaying plants, animals, and other organic material. A very large number of food chains exist in our ecosystem such as a grassland
Food Chains and Food Webs: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Biology Diagrams
In an ecosystem's intricate food chain, the primary producers capture the sun's energy through photosynthesis, paving the way for the primary consumers to feed on them. This leads to the emergence of the third trophic level, known as secondary consumers, which play a vital role by preying on the primary consumers. These secondary consumers become the prey of apex predators, the top predators

The Importance of Food Chains and Webs in Ecosystem Stability. Both food chains and food webs are integral to the functioning of ecosystems. They regulate populations, maintain balance, and help in nutrient cycling. Protecting critical species in a food web can help restore or maintain ecosystem balance. Agriculture:
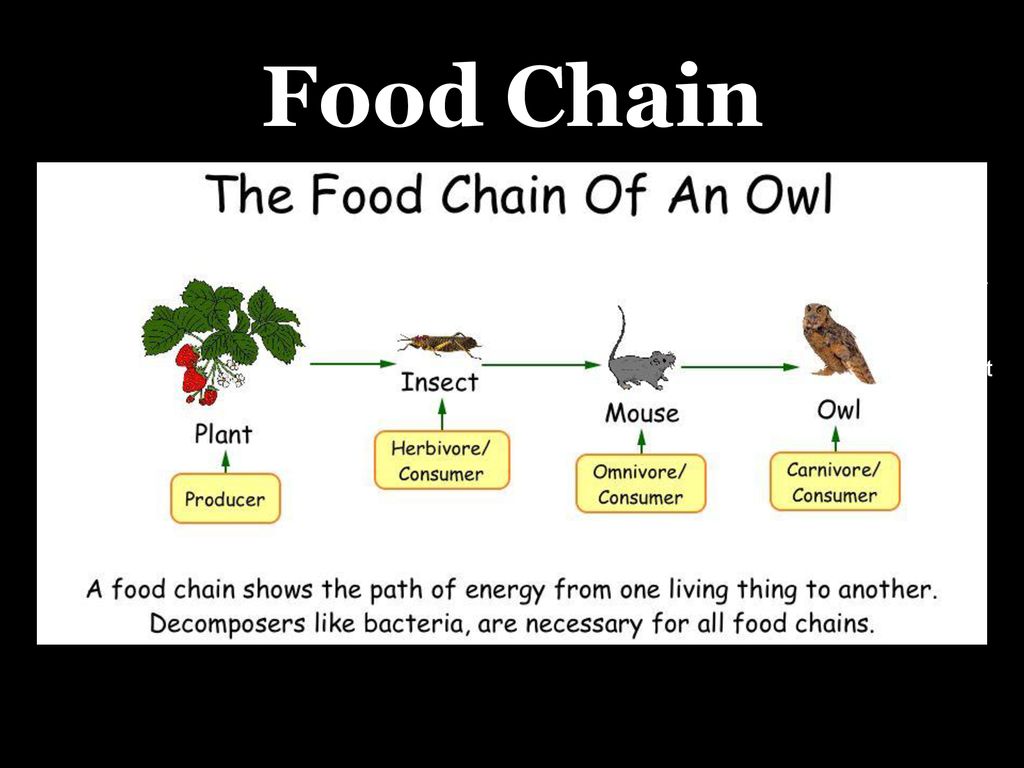
Food Chain: Energy Transfer And Ecosystem Balance Biology Diagrams
Ecosystem Balance: Food chains highlight the interdependence of species, where the decline of one species can disrupt the entire chain. Diverse Ecosystem Examples. Forest Food Chain Oak Tree (Producer) → Caterpillar (Primary Consumer) → Sparrow (Secondary Consumer) → Hawk (Tertiary Consumer)

Ecosystems have no particular size. An ecosystem can be small, like inside a tree trunk, medium like a pond, or large like the ocean. Food Chain. It is agreed that the living organisms need food to survive, but how do the living organisms in the ecosystem get food? The food chain explains how living things get the food they need.
