All Upper Limb Muscles Notes Drawings Biology Diagrams
All Upper Limb Muscles Notes Drawings Biology Diagrams Learn about the regions and structures of the upper limb, from the shoulder to the hand, with diagrams, quizzes and videos. Find out the origins, insertions, innervation and functions of the bones, joints, muscles and nerves of the upper extremity. Learn about the muscles, bones, blood supply and nerves of the shoulder, arm, forearm and hand with 3D models and videos. Explore the pectoral girdle, upper arm, elbow, wrist and hand anatomy in detail.

large V-shaped muscle on upper back origin: external occipital protuberance; superior nuchal line; spinous processes of C7-T12 insertion: clavicle; helps with forced inhalation when upper limb is fixed. pectoralis major. major chest muscle; adducts humerus medially; helps with forced inhalation when upper limb is fixed (interbicular groove) The upper limb comprises many muscles which are organized into anatomical compartments. These muscles act on the various joints of the hand, arm, and shoulder, maintaining tone, providing stability and allowing precise fluid movement.

Muscles of the Upper Limb (Upper Extremity): Anatomy & Diagram Biology Diagrams
A comprehensive list of muscles of the upper limb, including their origin, insertion, action, innervation, artery, and notes. Learn the anatomy and function of the muscles of the arm, forearm, hand, and fingers.
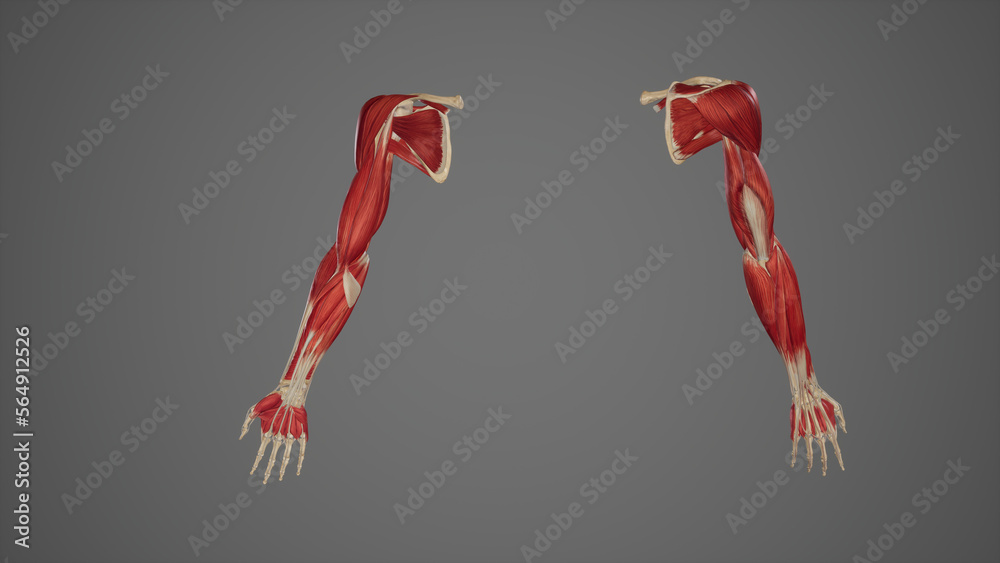
The muscles of the upper limb can be divided into 6 different regions: pectoral, shoulder, upper arm, anterior forearm, posterior forearm, and the hand.. There are 4 muscles of the pectoral region: pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior and subclavius.Collectively, these muscles are involved in movement and stabilisation of the scapula, as well as movements of the upper limb. Flexion (upper limb forwards past chest): Produced by the biceps brachii (both heads), pectoralis major, anterior deltoid, and corocobrachialis. Abduction (upper limb away from trunk, spreading arms wide): Produced by the supraspinatus and deltoid. Past 90 degrees, the scapula needs to be rotated by the trapezius and serratus anterior to

3D Interactive Anatomy Tutorials Biology Diagrams
The hand is a very mobile part of the upper limb, and we perform very specialised tasks with it every day, key adaptations can be seen in the specialised structures of the hand. In this section, learn more about the upper limb: Its bones, muscles, nerves, joints, blood vessels and lymphatics, anatomical areas, and structures found in the hand.
